It is well documented that high blood pressure is “the single largest risk factor” for death in the world.
Globally, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of mortality. Approximately 18 million people died from cardiovascular disease (CVDs) representing more than 30% of all global deaths.
By the year 2025, an estimated 1.6 billion of the world adult population will have hypertension. This is an increase of about 60% compared to the year 2000.
Although the most effective and quickest way to lower blood pressure is medication including the following: Beta Blockers (Atenolol, Metoprolol, Nebivolol and Propranolol), Ace Inhibitors (Benazepril, Captopril, Enalapril, Fosinopril and Lisinopril), Calcium Channel Blocker (Cardizem, Felodipine, Nifedipine and Verapamil), Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (Losartan, Olmesartan, Telmisartan and Valsartan) and Diuretics (Lasix, Hydrochlorothiazide, Indapamide and Metolazone), it is hard to believe that at least 80% of people are non-compliant and stop taking their medication.
The following is the average reduction in blood pressure of the above listed medications:
- Beta Blockers lowers blood pressure an average of -10 mmHg (SBP)/-8 mmHg DBP)
- Ace Inhibitors lowers blood pressure an average of 8mmHg (SBP)/-5 mmHg (DBP)
- Calcium Channel Blocker lowers blood pressure an average of 9.45 mmHg (SBP)
- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers lowers blood pressure an average of 8mmHg (SBP)/-5 mmHg (DBP)
- Diuretics lowers blood pressure an average of 7.9 mmHg (SBP/ -4.4 mmHg (DBP)
What is of significant importance is adding two tablespoons of flaxseed per day to your diet. (not flaxseed oil)
In an important peer reviewed study from the American Heart Association Journal, Hypertension, it was found that patients who entered the trial with a SBP ≥ 140 mm Hg at baseline obtained a significant reduction of 15 mm Hg in SBP and 7 mm Hg in DBP from flaxseed ingestion.
The magnitude of this decrease is as good or better than many blood pressures listed above.
Flaxseed induced one of the most potent antihypertensive effects achieved by a dietary intervention.
Indeed, the drop in blood pressure the researchers saw in the flaxseed study “was greater than the average decrease observed with the standard dose of anti-hypertensive medications.
In the above peer reviewed study patients (110 in total) ingested a variety of foods that contained 30 g of milled flaxseed or placebo each day over 6 months. Plasma levels of the alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) and enterolignans increased 2- to 50-fold in the flaxseed-fed group but did not increase significantly in the placebo group.
Most omega-6 fatty acids in the diet come from vegetable oils, such as linoleic acid (LA), not to be confused with alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is an omega-3 fatty acid.
The most evident reason for the benefits of flaxseeds and decreased blood pressure is thought be due to a change in plasma oxylipins.
What are oxylipins?
Oxylipins are a group of fatty acid metabolites involved in inflammation and have been implicated in many pro-inflammatory conditions, including aging and cardiovascular disease.
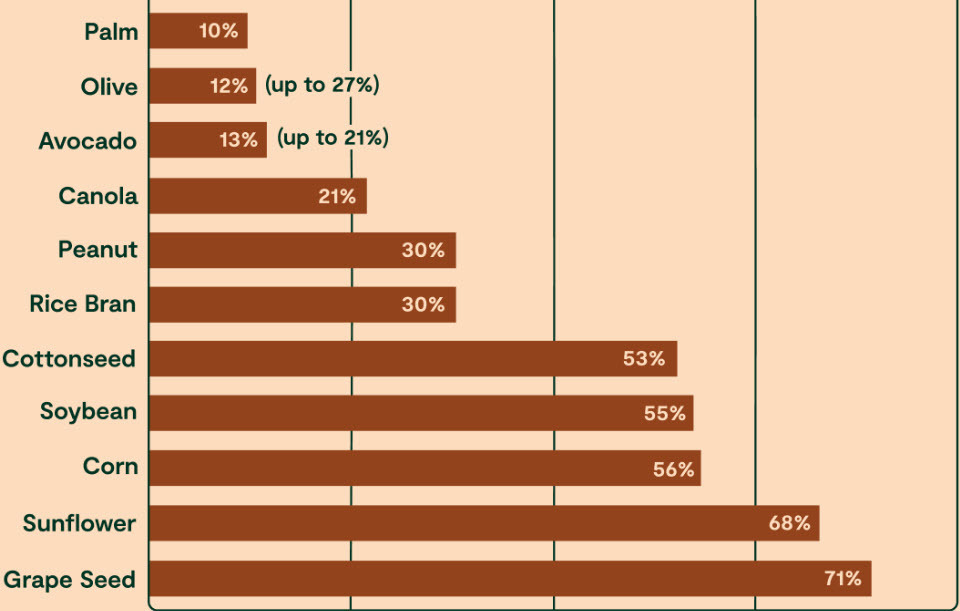
The best-characterized oxylipins associated with cardiovascular disease are derived from long-chain omega-6 fatty acid more commonly from linoleic acid. Linoleic acid oxylipins are often pro-inflammatory, associated with atherosclerosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and Alzheimer's disease. Centenarians have shown reduced levels of linoleic acid oxylipins in their blood circulation. Oxylipins are found preformed in animal products, particularly chicken and eggs, and can be made inside the body from junky oils rich in omega-6, such as cottonseed oil.
Here are oils to avoid and high in linoleic acid. Olive oil, avocado oil and palm oil are ok to consume on a limited basis but much better than the other oils listed above.
Elevated levels of pro-inflammatory, aging-associated oxylipins can be normalized by eating ground flaxseed.
Studies have shown that flaxseed consumption reduces blood pressure in patients with hypertension: by inhibiting the enzyme that makes these pro-inflammatory oxylipins. Eating flaxseeds inhibits the activity of the enzyme that makes these pro-inflammatory oxylipins, called leukotoxin diols, which in turn may lower blood pressure.
Dr. Grisanti's Comments:
Although it has been shown that flaxseeds have an influence on oxylipins it has been proposed that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. Each of the components of interest within flaxseed, ALA, lignans, fiber, and peptides—the omega-3s, the cancer-fighting lignans, all the soluble fiber, and the plant proteins, for instance all contribute towards BP reduction.
Although not all studies have shown significant blood pressure lowering effects of flaxseed consumption, there have been more than a dozen trials by now, involving more than a thousand subjects. When you put them all together there were “significant reductions in both SBP and DBP”—systolic blood pressure (the upper number) and diastolic blood pressure (the lower number) following supplementation with various flaxseed products.
Article courtey of Ronald Grisanti D.C., D.A.B.C.O., DACBN, MS, CFMP
References:
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02094
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34119421/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25740909/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6477925/
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD007451.pub2/full
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD010052.pub2/full
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD003823.pub2/full
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD003822.pub2/full
https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpheart.00201.2017
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6289399/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9552797/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25789320/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2951311/
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2021.645786/full
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10093787/://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25740909/
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03179
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1550830721000938
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/benefits-of-flaxseeds
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6707798/
** Always consult with a physician or healthcare practitioner with significant integrative or functional medicine training before starting any of the above recommendations.

Neal Lange
Contact Me